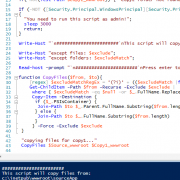
Terminate background stored procedure session
If you are executing background stored procedure, for example when run asynchronously by the Service Broker, there is often a need to stop the process, especially when it is time consuming operation. In order to do that, we have to find the session id of the process we want and then use KILL function to terminate it.
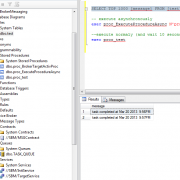
In order to display currently running queries let’s execute following.
SELECT sqltext.TEXT as SQLText, req.session_id, req.database_id, req.status, req.command, req.cpu_time, req.total_elapsed_time FROM sys.dm_exec_requests req CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(sql_handle) AS sqltext
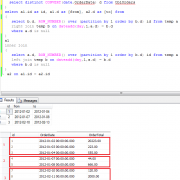
After we’ve seen how to display running queries, we can now create stored procedure allowing us to stop an session id related to the query name we want.
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[proc_com_KillBackgroundProcedure] (
@DatabaseName nvarchar(50) = '',
@ProcedureName nvarchar(50) = ''
)
AS
declare @SessionToBeKilled int = null;
declare @ProcessName nvarchar(max) = '';
declare dataset cursor for
select SQLText, session_id
from (SELECT sqltext.TEXT as SQLText,
req.session_id,
req.database_id,
req.status,
req.command,
req.cpu_time,
req.total_elapsed_time
FROM sys.dm_exec_requests req
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(sql_handle) AS sqltext
inner join master.dbo.sysdatabases m on m.dbid = database_id
where m.name = @databasename and req.status = 'background'
and [TEXT] like '%' + @ProcedureName + '%'
) as T
open dataset
fetch next from dataset into @ProcessName, @SessionToBeKilled
while @@fetch_status = 0
begin
EXEC('KILL ' + @SessionToBeKilled);
print 'killed: ' + convert(varchar(max),@SessionToBeKilled);
fetch next from dataset into @ProcessName, @SessionToBeKilled
end
close dataset
deallocate dataset
Above query simply gets the session id by the procedure name and then just kills the process. Be careful to not to kill an system query. I hope this has been useful for you 🙂